Escalation events
Escalation events are events which reference a named escalation, and are used to communicate to a higher flow scope. Unlike an error, an escalation event is non-critical and execution continues at the location of throwing.
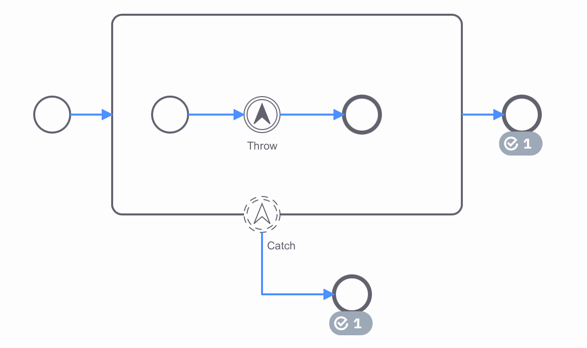
The example above shows the execution of an escalation event:
- The process reaches the
Throwevent. - This throws an escalation to a higher flow scope.
- The escalation is caught by the
Catchevent. - As escalation events are non-critical, the outgoing sequence flows of
ThrowandCatchare both taken.
Defining an escalation
In BPMN, an escalation event references an escalation. Escalations can be referenced by one or more escalation events.
An escalation must define an escalationCode. The value of this escalationCode is used to determine which catch event
can catch the thrown escalation.
For throwing escalation events, it is possible to define the escalationCode as an expression. When the event is reached, the expression is evaluated.
An escalation with the result of this expression is thrown. If no expression is used the statically defined escalationCode is used.
For catching escalation events it is not possible to use an expression. The escalationCode must always be a static value.
Alternatively, the escalationCode can be left empty. A catch event with an empty escalationCode will catch all thrown escalations.
Throwing the escalation
An escalation can be thrown by an escalation end event, or by an intermediate escalation throw event. Escalation events are non-critical. This means that if the throwing event has any outgoing sequence flows, they will be taken.
Catching the escalation
An escalation can be caught using a boundary event, or using an event subprocess. It is caught by one catch event at most, and this will be the catch event in the nearest parent flow scope.
It is not possible to define multiple escalation catch events with the same escalationCode in a single scope. It is also not permitted to have multiple escalation catch events without an escalationCode in a single scope.
The deployment gets rejected in these cases. However, it is possible to define both an escalation catch event with an
escalationCode and one without an escalationCode in the same scope. When this happens, the escalation catch event
that matches the escalationCode is prioritized.
If there are no escalation catch events that match the escalationCode, the escalation will not be caught. Unlike with
error events, no incident is raised. The process will continue without escalating.
Even though escalations are non-critical, it is still possible make escalation catch events interrupting. This will behave the same as other interrupting events. The catch event will terminate the scope it is attached to. In this case, the outgoing sequence flows of the throwing escalation event are not taken.
Additional resources
XML representation
An intermediate escalation throw event with expression:
<bpmn:intermediateThrowEvent id="StartEvent_1">
<bpmn:escalationEventDefinition id="EscalationEventDefinition_0sdm9od" escalationRef="Escalation_2alpsjo" />
</bpmn:intermediateThrowEvent>
<bpmn:escalation id="Escalation_2alpsjo" name="Escalation_2alpsjo" escalationCode="=escalationCode" />
An escalation boundary catch event:
<bpmn:boundaryEvent id="Event_1wpcmdz" cancelActivity="false" attachedToRef="Activity_1q7i1lv">
<bpmn:escalationEventDefinition id="EscalationEventDefinition_1fpge5i" escalationRef="Escalation_2alpsjo" />
</bpmn:boundaryEvent>
<bpmn:escalation id="Escalation_2alpsjo" name="Escalation_2alpsjo" escalationCode="escalationCode" />