Deciding about your stack
This best practice targets Camunda 8. For Camunda 7, please refer to Deciding about your Camunda 7 stack.
Our greenfield stack recommendation is a result of extensive discussions and evaluations. While not the only option, it is a solid choice if there are no specific reasons to choose an alternative.
Your choice of programming language should align with your team's expertise; we suggest Java or JavaScript for their broad applicability and support, and have outlined the Java greenfield stack below with Camunda 8 SaaS.
The Java greenfield stack
Spring Zeebe is currently a community-maintained project.
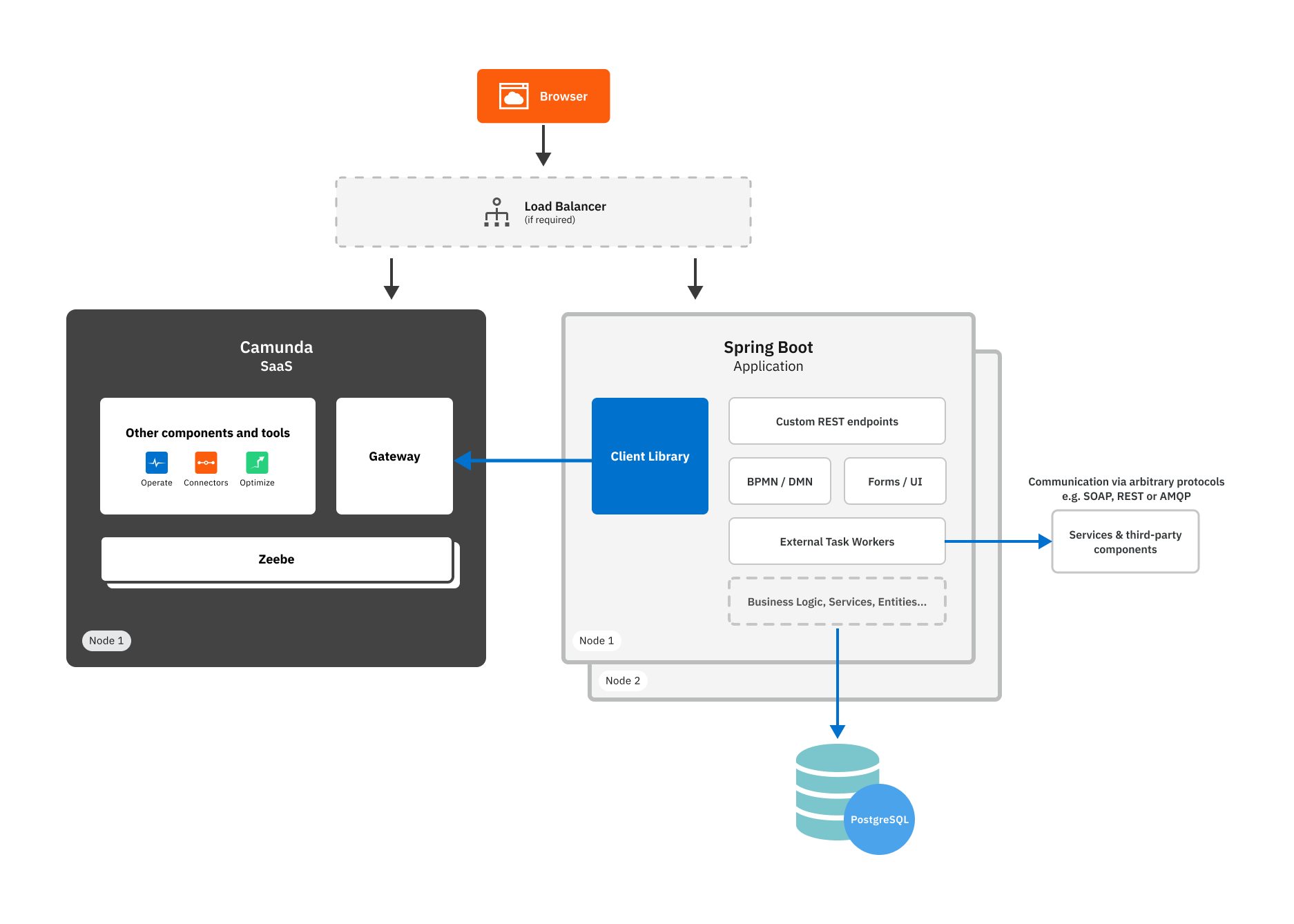
This architecture diagram illustrates the flow of requests from a user's browser through Camunda SaaS, where workflows and decisions are orchestrated. The process then moves to the Spring Boot application, which is responsible for executing business logic, handling database interactions with PostgreSQL, and managing various components such as custom REST endpoints, BPMN/DMN definitions, and external task workers.
Why this stack?
- SaaS simplifies workflow engine integration.
- Spring Boot is widely adopted for Java application development.
- Flexible for both on-premises and cloud environments.
Discover more in our getting started guide for microservices orchestration or the Spring Zeebe instructions.
Set up the stack
For a Java-based setup using Camunda 8 SaaS and Spring Boot, use the following stack:
Camunda 8 SaaS account and cluster
If you're new to Camunda SaaS, check out our getting started guide to set up your environment.
After signing up, create a cluster by following creating a cluster in Camunda 8, which provides step-by-step instructions on setting up a new cluster in the Camunda 8 environment.
Spring Boot
Develop your own process solutions as Spring Boot applications. This involves setting up a new Spring Boot project, either manually or using tools like Spring Initializr.
Integrate Spring Zeebe into the Spring Boot project by adding necessary dependencies to the project’s pom.xml file and configuring the application to use Camunda services.
Maven
Use Maven to manage the build lifecycle of the application.
IDE selection
Select an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) that supports Java development, Maven, and Spring Boot. Frequently used options include Visual Studio Code, IntelliJ IDEA, or Eclipse.
Java runtime
Install and use OpenJDK 17 as your Java runtime environment. Download it from the official JDK 17 download page.
Modeling
Download and use Camunda Modeler for designing and modeling business processes. Modeler is available here.
Code integration
Incorporate all Java code and BPMN process models into the Spring Boot project, ensuring that they are structured correctly and referenced properly within the application.
Run the process application:
To run the process application, transfer the jar to the desired server.
Start the application using the command java -jar YourProcessApplication.jar. Frequently, this deployment process is managed through Docker for ease of use.
For a practical implementation, refer to our example application on GitHub, which demonstrates a typical setup for a Spring Boot-based process application with Camunda.
Customize your stack
Polyglot stacks
You can develop process solutions as described with Java above also in any other programming language, including JavaScript. Use the existing language clients and SDKs for doing this.
Run Camunda 8 Self-Managed
Run Camunda 8 on your Kubernetes cluster. For local development, a Docker Compose configuration is available, though not for production use. Learn more in the deployment docs.